The transition from the Stone Age to the Bronze Age revolutionized tools, weapons, and everyday life. This era laid the foundation for the advancement of metallurgy, with bronze being the key material. In this article, we will explore how the Bronze Age shaped the use of metals www.metalswire.net and its lasting impact on technological progress.
Understanding the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age, which began around 3300 BCE and lasted until 1200 BCE, is defined by the widespread use of bronze—a blend of copper and tin—as a key material for tools and weapons. This era came after the Neolithic period, where stone tools dominated, and it set the stage for advanced civilizations to emerge, including the Sumerians, Egyptians, and the Indus Valley people. The discovery and use of metals during this period were transformative, influencing nearly every aspect of society, from agriculture to warfare.
The Development of Bronze and Its Advantages
Bronze was an alloy primarily made by combining copper with tin. This mixture produced a metal that was stronger and more durable than copper alone, making it ideal for crafting tools and weapons. The discovery of this process marked a crucial technological leap, enabling the creation of more effective tools that could perform a range of tasks more efficiently than their stone counterparts.
The use of bronze offered several advantages over earlier materials. It was more resistant to wear and tear, allowing for longer-lasting tools. It was also easier to cast into specific shapes, which meant that craftsmen could create more intricate designs and precise tools. The durability and malleability of bronze contributed significantly to the development of advanced societies, where tools and weapons were needed for construction, defense, and agriculture.

Impact on Weaponry and Warfare
One of the most notable impacts of the Bronze Age was its influence on weaponry and warfare. Bronze tools, such as swords, spears, and axes, were far superior to stone weapons in terms of durability and cutting ability. This change revolutionized how early civilizations fought wars and protected their territories.
Bronze weapons also gave rise to more organized and powerful military forces. With the creation of bronze armor and shields, warriors could fight more effectively and with greater protection. As a result, the Bronze Age saw the rise of professional armies and larger-scale conflicts between civilizations.
The development of weaponry during this period did not only have a military impact but also influenced trade and political power. The need for tin—a key component in the production of bronze—led to the establishment of trade routes, which connected distant regions and facilitated cultural exchanges. The availability and control of metal resources, especially tin, became a significant factor in determining the power of ancient kingdoms and empires.
The Influence of Bronze on Trade and Economy
The Bronze Age also saw the rise of complex trade networks. As bronze became a highly sought-after material, its production and distribution fostered international trade. Tin, which was necessary for making bronze, was not readily available in all regions, leading to trade routes that spanned vast distances. This led to the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies between different cultures.
The emergence of metallurgy also stimulated the growth of specialized industries. In areas where metalworking was prevalent, such as Mesopotamia, Egypt, and the Indus Valley, a new class of artisans and craftsmen emerged. These skilled workers played a critical role in the economy, supplying both everyday tools and intricate luxury items like jewelry and religious artifacts made of bronze.
The demand for bronze led to the growth of urban centers. As these cities expanded, they became hubs of production and trade. The surplus of bronze tools and weapons further encouraged the growth of agriculture, as better tools allowed farmers to work more efficiently. This, in turn, led to increased food production, population growth, and the rise of more complex societies.
The Bronze Age and Cultural Developments
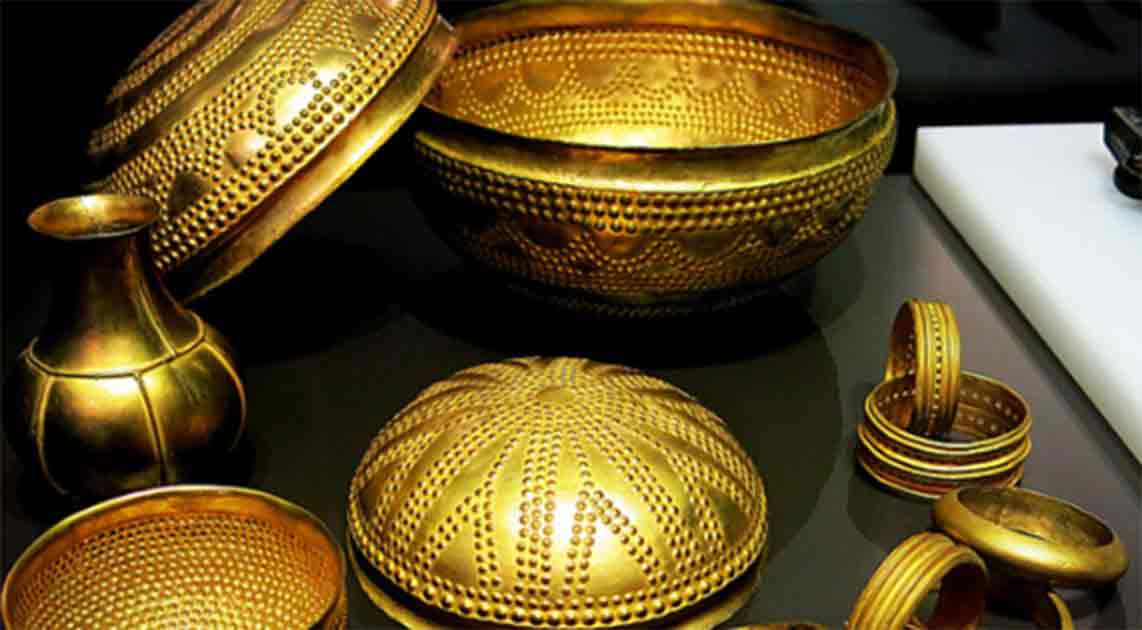
The influence of bronze extended beyond the practical realm and into the cultural and artistic domains. With the advancement in metalworking, civilizations could create not only tools and weapons but also intricate art pieces. Bronze was used to craft beautiful sculptures, ceremonial objects, and decorative items that reflected the cultural values and artistic tastes of the time.
For example, the Greeks used bronze for making statues that depicted gods, heroes, and famous historical figures. Similarly, in ancient China, bronze was used to create ritual vessels that were central to religious ceremonies. These cultural developments helped shape the identities of various civilizations and are still admired today for their craftsmanship and artistic value.

Legacy of the Bronze Age in Metal Use
The impact of the Bronze Age on metal use can still be felt today. The knowledge and techniques developed during this time laid the groundwork for the Iron Age, when iron became the dominant metal. The ability to extract and refine metals, learned during the Bronze Age, was crucial for advancing into the use of iron and other materials.
Moreover, the innovations in metallurgy during this period set the stage for modern industrialization. Today, the use of metals like steel, aluminum, and titanium has revolutionized construction, manufacturing, and technology. The lessons learned from the Bronze Age have shaped the development of materials science and continue to influence how metals are used in various industries.
Metals News and Modern Perspectives
In recent years, metals news has increasingly focused on advancements in metal alloys, recycling, and the exploration of alternative materials that can replace traditional metals. While we have moved far beyond the use of bronze, the legacy of the Bronze Age continues to influence the world of metallurgy. Researchers are constantly discovering new ways to improve the properties of metals, just as ancient civilizations did thousands of years ago.
The development of smart alloys and the growing emphasis on sustainable metal use are among the latest trends that echo the innovations of the past. As we look back at the Bronze Age, it is clear that this period of human history was a key milestone in the ongoing evolution of metal use, with far-reaching effects on technology, culture, and society.
Conclusion
The Bronze Age was a pivotal era in the history of metal use. The advancements in metallurgy during this period revolutionized tools, weapons, trade, and culture. From its influence on military technology to its impact on economic and social development, the Bronze Age played a crucial role in shaping the world we live in today. The legacy of bronze and its role in early civilizations continues to be felt, reminding us of the enduring power of metal throughout history.